SAVE MODBUS VARIABLE LIST 20210301 REV36
Table Of Contents
- 1 Information
- 2 Modbus variable list
- 2.1 Demand Control
- 2.2 User modes
- 2.3 Airflow Control
- 2.4 Outdoor Airflow Compensation
- 2.5 Temperature Control
- 2.6 Cooler
- 2.7 Heater
- 2.8 Extra Controller
- 2.9 Change-over (Heating/Cooling)
- 2.10 Moisture transfer control
- 2.11 Cooling recovery
- 2.12 ECO mode
- 2.13 Free Cooling
- 2.14 Week Schedule
- 2.15 Time and Date
- 2.16 Filter replacement
- 2.17 Analog Input values (Temperatures, CO2, RH)
- 2.18 Digital Input functions
- 2.19 Output values
- 2.20 Alarms
- 2.21 System settings
- 2.22 Modbus
- 2.23 Unit Backups
- 3 Revision table
Information |
1
1 Information
Modbus is a serial communication protocol used for transmitting information over serial lines between electronic devi-
ces. The device requesting the information is called “Master”, while devices supplying the requested information are
“Slaves”. When it comes to planning data communication for open, multi-vendor industrial control systems, Modbus is
the first choice of end users and integrators alike.
The Modbus/RTU protocol defines how a “master” device polls one or more “slave” devices to read and write data in
real time by means of RS232, RS422, or RS485 serial data communication. Modbus/TCP, an extension of Modbus/RTU,
defines how Modbus/RTU and Modbus/ASCII messages are encoded within and transported over TCP/IP-based net-
works. Modbus/TCP is just as simple to implement and flexible to apply as the original Modbus/RTU.
1.1 Physical layer
New Systemair controls have standard and readily available Modbus/RTU over three-wire (A, B and GND) RS485 on the
Connection Board (CB) and Modbus/TCP over TCP/IP using Internet Access Module (available as an accessory - Art. No.
211243). For Modbus/TCP connection over TCP/IP using Internet Access Module refer to the IAM quick guide.
Slave address: 1 to 247
Baud rate: 9600 to 115200
Parity: None, Even, Odd
Stop bits: 1 (fixed)
Parameters can be changed in Modbus page (Service -> Communication -> Modbus) in the Control Panel.
1.2 Transmission modes
The registers are Input registers (read-only) and Holding registers (read-write) when using Modbus/RTU and Holding
registers (read-write) when using Modbus/TCP.
All registers are 16 bit Integers.
Table 1 Signal types used
Unsigned Integers
I
Signed Integers
I*
Table 2 Register types used
Input Registers
16-bit quantity, Analog Input Register provided by an I/O system, read-only, Modbus Function
04
Holding registers 16-bit quantity, analog output HR alterable by an application program, read-write , Modbus
function 03 / 06 / 16
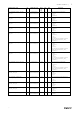
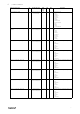
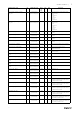
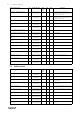
2 Modbus variable list
Tables below provides an extensive list of Modbus variables used in the system grouped according to the functionality
the variables are related to.
2.1 Demand Control
Symbolic register name
Sig.
Modbus Reg. type Mod-
bus
Adr.
Min Max Description
REG_DEMC_RH_HIGHEST I
Read Input Register
(Function 04)
1001 0 100
Highest value of all RH sensors
REG_DEMC_CO2_HIGHEST I
Read Input Register
(Function 04)
1002 0 2000
Highest value of all CO2 sensors
REG_DEMC_RH_PI_SP I
Read Input Register
(Function 04)
1011 0 100
Set point for RH demand control
REG_DEMC_RH_PI_FEEDBACK I
Read Input Register
(Function 04)
1012 0 100
Sensor value for RH demand control
REG_DEMC_RH_PI_OUTPUT I
Read Input Register
(Function 04)
1019
Output value for RH demand control.(1):
Depends on regulation type. Value can be
%, RPM, Pressure or Flow
| 2.1