Datasheet
BANDWIDTH
System bandwidth determines an oscilloscope’s ability to measure an analog
signal. Specifically it determines the maximum frequency that the instrument can
accurately measure. Bandwidth is also a key determining factor in price.
Determine what you need
For example, a 100 MHz oscilloscope is usually guaranteed to have less than 30%
attenuation at 100 MHz. To ensure better than 2% amplitude accuracy, inputs should be
lower than 20 MHz.
For digital signals, measuring rise and fall time is key. Bandwidth, along with sample rate,
determines the smallest rise-time that an oscilloscope can measure.
The probe and oscilloscope form a measurement system that has an overall bandwidth.
Using a low-bandwidth probe will lower the overall bandwidth so be sure to use probes
that are matched to the scope.
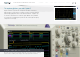
Bandwidth is defined as the frequency at which a sine-wave
input signal is attenuated to 70.7% of its true amplitude (the
-3 dB or ‘half-power’ point, shown here for a 100 MHz scope).
100
85
70.7
10 50
Frequency (MHz)
30% Amplitude degradation!
Amplitude error (%)
100
-3 dB
~2% Amplitude degradation
4
10 FACTORS IN CHOOSING A BASIC OSCILLOSCOPE
CONTENTS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
CONTACTINTRO
ß
www.tektronix.com