User manual
www.ti.com
Mapregion1
Mapregion2
Mapregion3
Mapregion4
0400:0000
0800:0000
07FF:FFFF
0800:0100
0800:00FF
0801:0100
0801:00FF
0841:00FF
Mapregion1
Mapregion2
Mapregion3
Mapregion4
Localdevice
Remote
VLYNQdevice
0000:0000
03FF:FFFF
0400:0000
0400:00FF
0500:0000
0500:FFFF
0B00:0000
0B3F:FFFF
Peripheral Architecture
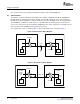
In the local device, the address of the VLYNQ remote memory map in the local configuration space is the
transmit address accessing remote devices over the serial interface. The address of the VLYNQ remote
memory map is programmed in the TX address map register (XAM). When the local device transmits, first
it strips off the transmit address offset in the local device memory map. Then, the local device sends the
data with an address offset from the transmit address.
VLYNQ allows each receive packet address to be translated into one of four mapped regions. No
restriction is placed on the size or on the offset of each mapped region, except that each must be aligned
to 32-bit words.
The transmitted address is used to determine which remote mapped region is being accessed at the
remote device. This is achieved by summing each memory size sequentially until the memory size is
larger than the transmitted address. The last memory size that is added is the targeted region. A memory
size and an offset specify the remote map. The remote map is programmed in the RX address map size
register (RAMS n) and in the RX address map offset (RAMO n) in the remote device.
Figure 7. Example Address Memory Map
18 VLYNQ Port SPRUF89 – October 2007
Submit Documentation Feedback