Calculator User Manual
158 Chapter 10: 3D Graphing
10_3D.DOC TI-89/TI-92 Plus: 3D Graphing (English) Susan Gullord Revised: 02/23/01 11:00 AM Printed: 02/23/01 4:22 PM Page 158 of 2210_3D.DOC TI-89/TI-92 Plus: 3D Graphing (English) Susan Gullord Revised: 02/23/01 11:00 AM Printed: 02/23/01 4:22 PM Page 158 of 22
The Window Editor maintains an independent set of Window
variables for each
Graph
mode setting (just as the Y= Editor
maintains independent function lists). 3D graphs use the following
Window variables.
Variable Description
eye
q
, eye
f
,
eye
ψ
Angles (always in degrees) used to view the graph.
Refer to “Rotating and/or Elevating the Viewing Angle”
on page 162.
xmin
,
xmax
,
ymin
,
ymax,
zmin, zmax
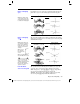
Boundaries of the viewing cube.
xgrid, ygrid
The distance between
xmin
and
xmax
and between
ymin
and
ymax
is divided into the specified number of grids.
The
z(x,y)
equation is evaluated at each grid point
where the grid lines (or grid wires) intersect.
The incremental value along
x
and
y
is calculated as:
x increment =
xmax
ì
xmin
xgrid
y increment =
ymax
ì
ymin
ygrid
The number of grid wires is
xgrid + 1
and
ygrid + 1
. For
example, when
xgrid = 14
and
ygrid = 14
, the xy grid
consists of 225 (15
×
15) grid points.
ncontour
The number of contours evenly distributed along the
displayed range of z values. Refer to page 168.
Standard values (set when you select
6:ZoomStd
from the
„
Zoom
toolbar menu) are:
eye
q
= 20.
xmin =
ë
10. ymin =
ë
10. zmin =
ë
10.
eye
f
= 70. xmax = 10. ymax = 10. zmax = 10.
eye
ψ
= 0. xgrid = 14. ygrid = 14. ncontour = 5.
You may need to increase the standard values for the
grid
variables
(
xgrid
,
ygrid
) to ensure that enough points are plotted.
Window Variables
Note: If you enter a
fractional number for
xgrid
or
ygrid
, it is rounded to the
nearest whole number
‚
1.
Note: The 3D mode does
not have scl Window
variables, so you cannot set
tick marks on the axes.
Note: Increasing the grid
variables decreases the
graphing speed.
z(xmin,ymax)
z(xmax,ymin)
z(xmin,ymin)
z(xmax,ymax)