Datasheet
www.ti.com
DYNAMIC VOLTAGE POSITIONING
SOFT START
LOW DROPOUT OPERATION 100% DUTY CYCLE
Vin
min
+ Vout
max
) Iout
max
ǒ
r
ds
(ON)
max
) R
L
Ǔ
Iout
max
= maximum output current plus inductor ripple current
r
ds
(ON)
max
= maximum P-channel switch r
ds
(ON)
R
L
= DC resistance of the inductor
Vout
max
= nominal output voltage plus maximum output voltage tolerance
ENABLE
UNDERVOLTAGE LOCKOUT
TPS62200 , , TPS62201
TPS62202 , TPS62203 , TPS62207
TPS62204 , TPS62205 , TPS62208
SLVS417E – MARCH 2002 – REVISED MAY 2006
DETAILED DESCRIPTION (continued)
As described in the power save mode operation sections and as detailed in Figure 2 , the output voltage is
typically 0.8% above the nominal output voltage at light load currents, as the device is in power save mode. This
gives additional headroom for the voltage drop during a load transient from light load to full load. During a load
transient from full load to light load, the voltage overshoot is also minimized due to active regulation turning on
the N-channel rectifier switch.
The TPS6220x has an internal soft start circuit that limits the inrush current during start-up. This prevents
possible voltage drops of the input voltage in case a battery or a high impedance power source is connected to
the input of the TPS6220x.
The soft start is implemented as a digital circuit increasing the switch current in steps of typically 60 mA,120 mA,
240 mA and then the typical switch current limit of 480 mA. Therefore the start-up time mainly depends on the
output capacitor and load current. Typical start-up time with 10 µF output capacitor and 200 mA load current is
800 µs.
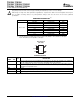
The TPS6220x offers a low input to output voltage difference, while still maintaining operation with the 100%
duty cycle mode. In this mode, the P-channel switch is constantly turned on. This is particularly useful in battery
powered applications to achieve longest operation time by taking full advantage of the whole battery voltage
range. The minimum input voltage to maintain regulation, depending on the load current and output voltage, can
be calculated as
Pulling the enable low forces the part into shutdown, with a shutdown quiescent current of typically 0.1 µA. In
this mode, the P-channel switch and N-channel rectifier are turned off, the internal resistor feedback divider is
disconnected, and the whole device is in shutdown mode. If an output voltage, which could be an external
voltage source or super cap, is present during shutdown, the reverse leakage current is specified under
electrical characteristics. For proper operation the enable pin must be terminated and must not be left floating.
Pulling the enable high starts up the TPS6220x with the soft start as previously described.
The undervoltage lockout circuit prevents the device from misoperation at low input voltages. It prevents the
converter from turning on the switch or rectifier MOSFET under undefined conditions.
5
Submit Documentation Feedback