User's Manual
Table Of Contents
- Package Contents
- Chapter 1. Product Overview
- Chapter 2. Connecting the Modem Router
- Chapter 3. Quick Installation Guide
- Chapter 4. Configuring the Modem Router
- 4.1 Login
- 4.2 Status
- 4.3 Quick Setup
- 4.4 Operation Mode
- 4.5 Network
- 4.6 IPTV
- 4.7 DHCP Server
- 4.8 Wireless 2.4GHz
- 4.9 Wireless 5GHz
- 4.10 Guest Network
- 4.11 USB Settings
- 4.12 Route Settings
- 4.13 IPv6 Route Settings
- 4.14 Forwarding
- 4.15 Parental Control
- 4.16 Firewall
- 4.17 IPv6 Firewall
- 4.18 IPv6 Tunnel
- 4.19 Bandwidth Control
- 4.20 IP&MAC Binding
- 4.21 Dynamic DNS
- 4.22 Diagnostic
- 4.23 System Tools
- 4.24 Logout
- Appendix A: Specifications
- Appendix B: Troubleshooting
- Appendix C: Technical Support
Archer D2
AC750 Wireless Dual Band Gigabit ADSL2+ Modem Router User Guide
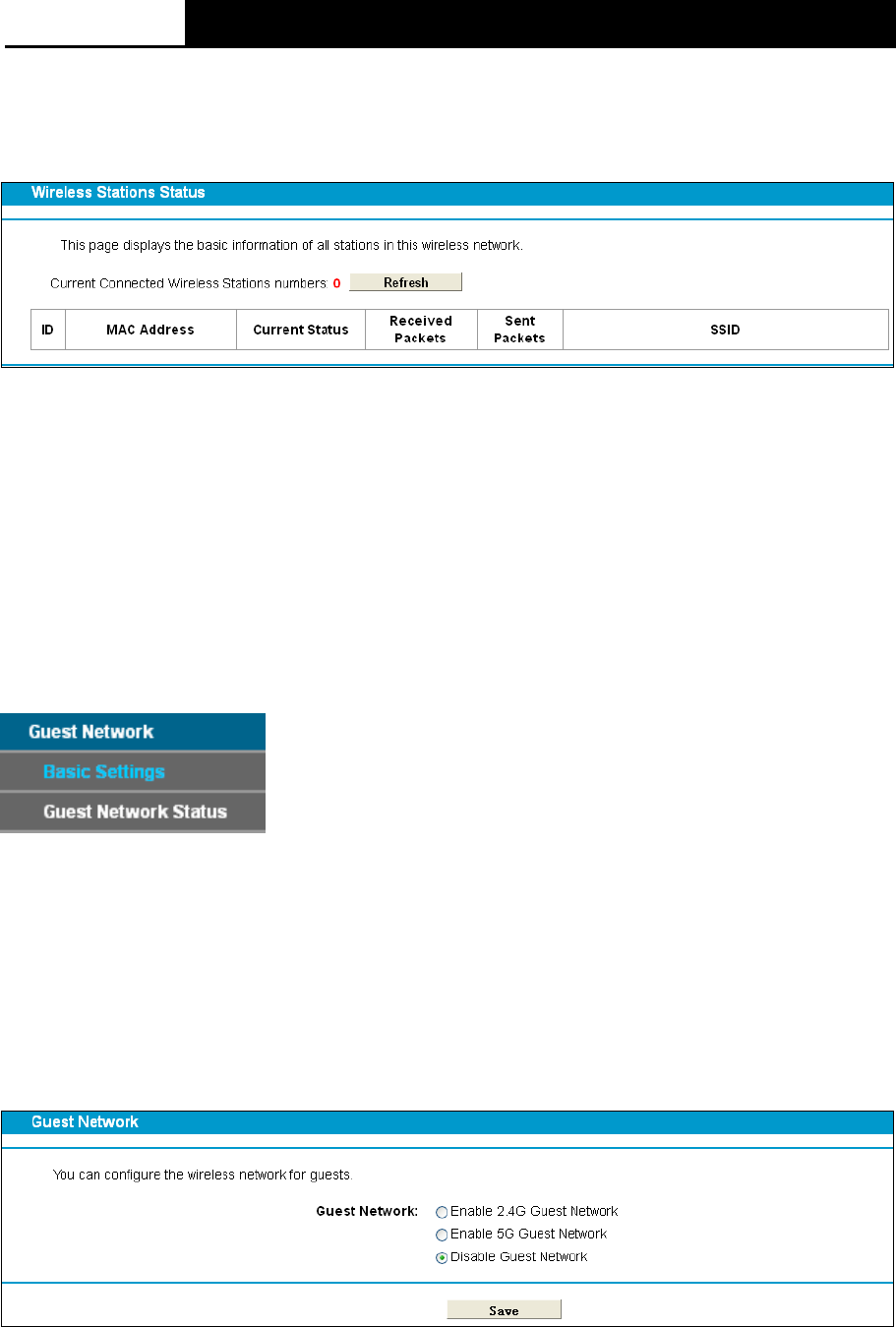
4.9.7 Wireless Status
Choose menu “Wireless 5GHz””Wireless Status”, you can see the MAC Address, Current
Status, Received Packets and Sent Packets for each connected wireless station.
Figure 4-50
MAC Address: The connected wireless station's MAC address
Current Status: The connected wireless station's running status, one of STA-AUTH/
STA-ASSOC/ STA-JOINED/ WPA/ WPA-PSK/ WPA2/ WPA2-PSK/ AP-UP/ AP-DOWN/ Disconnected
Received Packets: Packets received by the station
Sent Packets: Packets sent by the station
Click on the Refresh button to update this page.
4.10 Guest Network
There are two submenus under the Guest Network menu: Basic Settings and Guest Network
Status. Click any of them, and you will be able to scan or configure the corresponding function.
The detailed explanations for each submenu are provided below.
4.10.1 Basic Settings
Choose menu “Guest Network”“Basic Settings”, and you will see the screen as shown in
Figure 4-51. This feature allows you to create a separate network for your guests without allowing
them to access your main network and the computers connected to it.
Figure 4-51
Enable 2.4G Guest Network: Check this box to enable 2.4G Guest Network. And you can
set wireless parameters for 2.4G guest network as shown in Figure 4-52.
61










