User's Guide
Table Of Contents
- Web Smart Switch Series Product Overview
- Switch Installation
- Accessing switch management interfaces
- System
- Network
- QoS (Quality of Service)
- Security
- Tools
- Using the Web Smart Switch Management Utility
- Hardware Features and Specifications
- Web Smart Switch Series Software & Technical Specifications
- Quick Installation GuideTroubleshooting
- Appendix
© Copyright 2018 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
41
TRENDnet User’s Guide
Web Smart Switch Series
Spanning Tree
Protocol
Network > Spanning Tree > Protocol
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) provides network topology for any arrangement of
bridges/switches. STP also provides a single path between end stations on a network,
eliminating loops. Loops occur when alternate routes exist between hosts. Loops in an
extended network can cause bridges to forward traffic indefinitely, resulting in
increased traffic and reducing network efficiency.
1. Log into your switch management page (see “Access your switch management page”
on page 5).
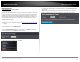
2. Click on Network, click on Spanning Tree, and click on Protocol.
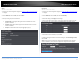
3. Review the settings. Click Apply to save changes.
Global STP Status: Select the STP state on the device. The possible field values
are:
o Disable – Disables STP on the device. This is the default value.
o Enable – Enables STP on the device.
Protocol Version: Specifies the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) mode to enable
on the switch. The possible field values are:
o STP – Enables STP 802.1d on the device.
o RSTP – Enables Rapid STP 802.1w on the device. This is the default
value.
o MSTP – Enables Multiple STP 802.1s on the device.
Bridge Priority: The Bridge Priority has a range 0 to 61440 in increments of
4096. To make this easier for you, the Web Management Utility divides the
range into increments. You specify the increment that represents the desired
bridge priority value.
Maximum Age: The Maximum Age defines the amount of time a port will wait
for STP/RSTP information. MSTP uses this parameter when interacting with
STP/RSTP domains on the boundary ports. Its range is 6 - 40 seconds
Hello Time: The Hello Time is frequency with which the root bridge sends out a
BPDU.
Forward Delay: The Forward Delay defines the time that the bridge spends in
the listening and learning states. Its range is 4 - 30 seconds.
Transmit Hold Count: The Transmit Hold Count specifies the maximum number
of BPDUs that the bridge can send per second. Its range is 1 - 10.
Max Hop Count: The Max Hop Count is a parameter set in a BPDU packet when
it originates. It is decremented by 1each time it is retransmitted by the next
bridge. When the Hop Count value reaches zero, the bridge drops the BPDU
packet. Its range is 6 - 40 hops.
In addition, this section also displays the spanning tree root information.