Data Sheet
MPU-6000/MPU-6050 Product Specification
Document Number: PS-MPU-6000A-00
Revision: 3.4
Release Date: 08/19/2013
35 of 52
Communications
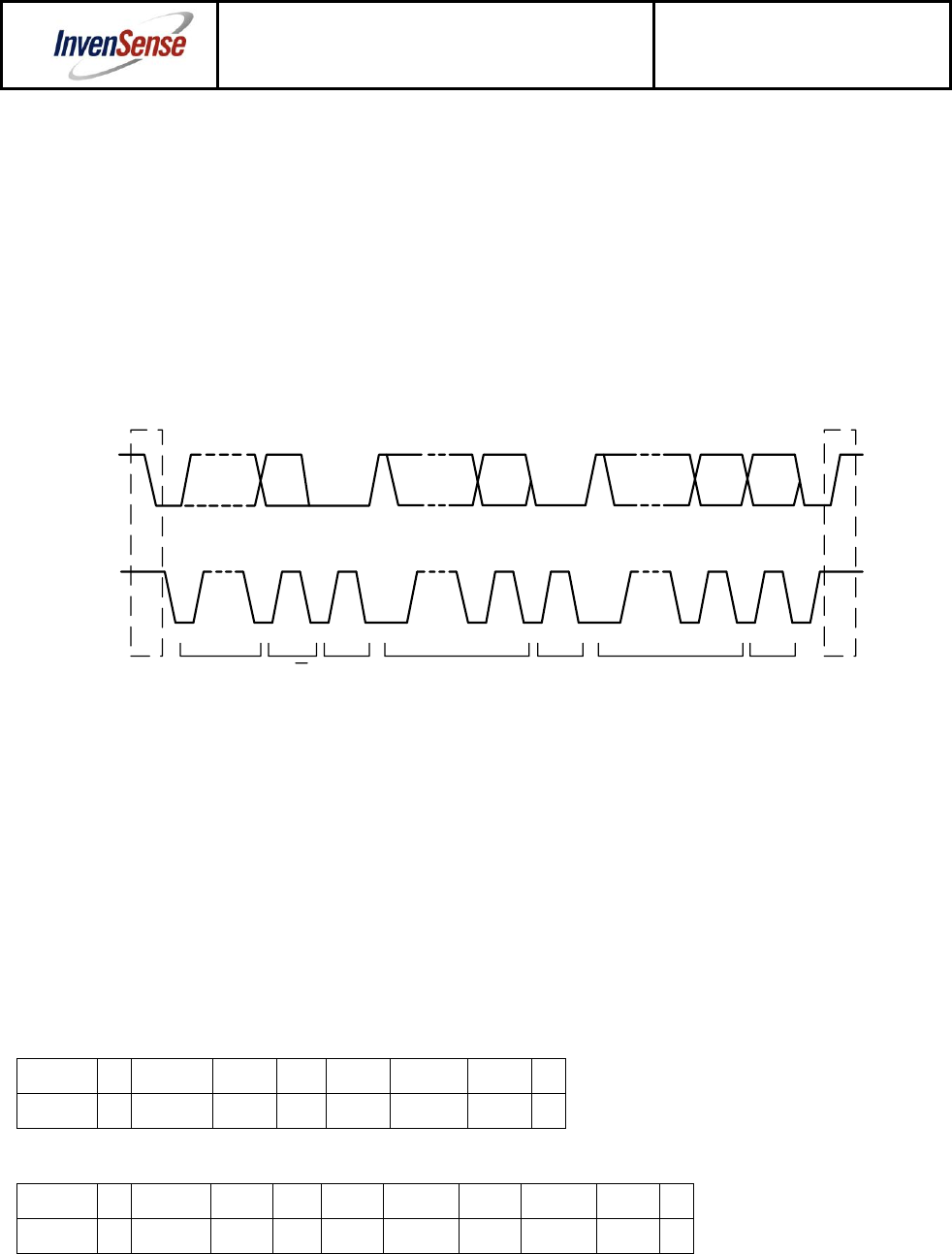
After beginning communications with the START condition (S), the master sends a 7-bit slave address
followed by an 8
th
bit, the read/write bit. The read/write bit indicates whether the master is receiving data from
or is writing to the slave device. Then, the master releases the SDA line and waits for the acknowledge
signal (ACK) from the slave device. Each byte transferred must be followed by an acknowledge bit. To
acknowledge, the slave device pulls the SDA line LOW and keeps it LOW for the high period of the SCL line.
Data transmission is always terminated by the master with a STOP condition (P), thus freeing the
communications line. However, the master can generate a repeated START condition (Sr), and address
another slave without first generating a STOP condition (P). A LOW to HIGH transition on the SDA line while
SCL is HIGH defines the stop condition. All SDA changes should take place when SCL is low, with the
exception of start and stop conditions.
SDA
START
condition
SCL
ADDRESS R/W ACK DATA ACK DATA ACK
STOP
condition
S P
1 – 7 8 9 1 – 7 8 9 1 – 7 8 9
Complete I
2
C Data Transfer
To write the internal MPU-60X0 registers, the master transmits the start condition (S), followed by the I
2
C
address and the write bit (0). At the 9
th
clock cycle (when the clock is high), the MPU-60X0 acknowledges the
transfer. Then the master puts the register address (RA) on the bus. After the MPU-60X0 acknowledges the
reception of the register address, the master puts the register data onto the bus. This is followed by the ACK
signal, and data transfer may be concluded by the stop condition (P). To write multiple bytes after the last
ACK signal, the master can continue outputting data rather than transmitting a stop signal. In this case, the
MPU-60X0 automatically increments the register address and loads the data to the appropriate register. The
following figures show single and two-byte write sequences.
Single-Byte Write Sequence
Burst Write Sequence
Master
S
AD+W
RA
DATA
P
Slave
ACK
ACK
ACK
Master
S
AD+W
RA
DATA
DATA
P
Slave
ACK
ACK
ACK
ACK