Specifications
EISA and ISA Bus Support
14.7 EISA Bus Support on DEC 2000
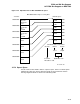
Figure 14–3 DEC 2000 Address Map
0 0000 0000
EISA memory address space
0000 0000
0000
EISA I/O address space
ZK−6741A−GE
0 0FFF FFFF
2 0000 0000
2 0600 0000
2 0080 0000
3 0000 0000
3 0008 0000
3 0010 0000
EISA
memory
slot 2 slot
specific I/O
512 KB
DE422 slot
specific
I/O 512 KB
EISA I/O
system
board
DE422
memory
buffer
8 MB
EISA
memory
Host
memory
256 MB
etc
DE422 slot
specific I/O
System
board
slot 2
slot 3
DE422
memory
buffer
64 KB
000C 0000
000C FFFF
000D 0000
1000
2000
3000
etc
14.7.1.9 EISA I/O Space Access (3.0000.0000 - 3.FFFF.FFFF)
EISA I/O space is mapped into the address space accessed by CPU addresses
3.0000.0000 thru 3.FFFF.FFFF. As mentioned in the historical discussion of
the EISA/ISA busses, the cards in the system decode only 10 I/O address bits,
with the EISA cards using bits <15:12> to provide geographical addressing (they
choose the slot the reference is directed to). Because each slot can take up a
maximum of 4 Kbytes, the maximum I/O space needed on this system is 64
Kbytes. Unfortunately, this requirement gets shifted up by 7 bits and turns into
8 Mbytes of EISA I/O address space. Because the Compaq VGA card will address
registers on all of the 16 slots of EISA I/O space, all 64 Kbytes must be mapped.
An expanded view of the mapping of EISA I/O space to the DEC 2000 Address
Map is shown on the following page. As an example of how the address for an
EISA I/O space access is formed, assume that the Adaptech 1742a board is in
14–11