User's Manual Part 3
PERFORMING DOWNLOADS
Omni 3600 Download Differences
O
MNI 3600 REFERENCE MANUAL 71
The processing routine gives you both visible and audible indications if a
specific certificate successfully authenticates. The file authentication module
does not halt the process if a certificate fails to authenticate, but continues to
the next step: authenticating signature files.
If one or more certificates fail to authenticate, the ensuing file authentication
process based on signature files probably also fails, with the result that an
application is not authenticated and is not allowed to execute on the terminal.
When a certificate file is authenticated, the data it contains is added to the
certificate tree and the certificate file is deleted from the RAM. When all
required certificates are authenticated and stored in the certificate tree, the file
authentication process for signature files can proceed.
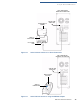
Figure 30 Display Prompts During the File Authentication Process
5 Signature files are processed next (after certificate files). The file
authentication module calls the signature checking routine one time for each
new signature file it detects. Each *.p7s file is checked as it is detected; a list is
not built and multiple processing passes are not required.
• If a signature file is authenticated, the “AUTHENTIC” message displays and
the target file’s ATTR_NOT_AUTH bit is set to 1.
• If the authentication process fails, the “FAILED” message displays for five
seconds and the terminal beeps three times (see Figure 30). The routine
then continues processing the next signature file until all newly detected
signature files are checked.
• If a signature file fails to authenticate and its target file is an executable
code file, such as *.out or *.lib, the executable is not allowed to run on the
terminal on terminal restart.