Operating instructions
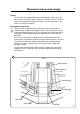
Mechanical and electrical design
31
32
1153
1154
F
F
Drive motor
Description in general
The motor is mounted on an axle with rubber
dampeners.
The V-belt is tightened by turning the motor on
the axle and locking it in place using the tightener
on the rear side of the motor. The motor and
tightener unit have vibration and noise
dampening rubber suspensions.
Construction in general
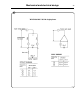
The motor consists of stator, rotor and end-
shields with ball-bearings. The stator and the
rotor consists of plates, insulated from each other
and welded together. The stator is provided with
slots in which the 2-pole and 18-pole windings
are wound. The windings are impregnated with a
temperature-resistant sound-insulating resin
varnish according to class B. The end-shields are
die-cast. The ball bearings are permanently
lubricated.
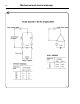
Construction of single-phase motor
Single-phase motors have an 18-pole winding
(wash-speed) the same as three-phase motors,
using a continous connected capacitor, while the
2-pole winding (extract-speed) is a specially
designed winding with both continous connected
capacitor and starting capacitor.
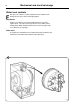
Function of 3-phase motor
When the stator winding is charged, a magnetic
field will occur, which in turn will rotate the rotor
at a fixed RPM depending upon the number of
poles in the winding. The 18-pole winding gives
the wash speed and the 2-pole winding the
extract-speed. When operating with load, the
speed deviates slightly from the synchronous
(no-load) speed. This difference is called the slip
and is usually expressed as a percentage of the
syncronous speed. The motors will work satisfac-
torily at nominal voltage +10%-15%.
Function of single-phase motor
When the stator winding is charged without a
capacitor, two counteracting magnetic fields are
created. When a capacitor is connected, it will
displace one of the two magnetic fields adding it
to the other, creating a torque turning the rotor in
a specific direction. The RPM is the same as for
the 3-phase motor.
21