SoundGrid Studio User Guide / Owners Manual
Table Of Contents
- Welcome to SoundGrid Studio
- Part 1: Getting Started
- Part 2: Top Bar
- Part 3: Setup Window
- Setup Window Overview
- Network Controls
- Device Racks: Assigning and Managing Network Devices
- I/O Devices Racks
- I/O Device Racks Displays and Controls
- I/O Devices Menu Items
- SG Connect
- I/O Sharing
- Connected Systems
- System Inventory in Super Systems
- Sharing a Device
- Setting up Device Sharing
- Shared Devices: Clocking Considerations
- Patching Shared Devices
- Patching Shared Output Devices
- Shared and Un-Shared Devices in the Patch
- Removing Shared Devices
- If the Sharing Host Becomes Unavailable
- Share Preamp Control
- Servers
- External Control Devices
- Setting Sample Rate
- Assigning I/O Devices Manually
- Working Offline
- Mixer Settings
- User Interface Settings Section
- Patch Window Sections
- The Patch Grid
- Mixer Layers
- Mixer Channels
- Mixer Layer Modes
- Using Plugins
- Monitor Panel
- INCORPORATING MIDI
- MACKIE CONTROL PROTOCOL
- Setting Up Mackie HUI in a DAW
- Setup Window Overview
- Part 4: Patch Window
- Part 5: Mixer Window
- Appendix
Part 3: Setup Window
SoundGrid Studio/ User Guide
46
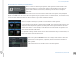
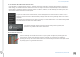
Shared and Un-Shared Devices in the Patch
B-IOS, owned by System #1 System #2, using shared device B-IOS
Device B-IOS appears as an assigned device
in the output patch of System #1 (left) and as
a shared remote device in System #2 (right).
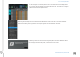
When an output patch is made in either system, the corresponding I/O channel in the other system is
colored orange to indicate that the patch is in use.
System #1 (left): Analog line outs 6 and 8 are
orange, indicating that those channels have
been claimed by another system, in this case,
System #2. Local patches are shown in green.
System #2 (right): Analog line outs 1, 2, 4,
and 5; headphones 2L and 2R; AES 1 and 2
are patched by System #1, the device
manager. Therefore, they are unavailable for
patching by other systems.
A manager can always disconnect an I/O channel and establish its own connection.