User Manual
Multichannel Monitoring Tutorial Booklet (M2TB) rev. 3.5.2
Masataka Nakahara : SONA Corporation
©2005 YAMAHA Corporation, ©2005 SONA Corporation
10 / 74
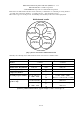
Each format of multi-channel media is characterized by a combination of “surround processing method,”
“encoding and compression method,” “recording response,” and “playback response.”
Most of these types of media provide “downmixing” functionality to allow two-channel playback.
[Fig. 3] Factors that feature multichannel media
Currently, the following major multi-channel formats exist as mass consumer media.
Media Video cassette tape, etc.
Method 3-1 matrix 5.0 matrix
Name Dolby Surround
DTS Stereo
Dolby Pro Logic II
Manufacturer, Organization Dolby lab. DTSDolby lab.
Surround processing method 4-2 Matrix Encode 5-2 Matrix Encode
Compression method -- -
Recording response (media)
L, C, R: full range
S: 100Hz - 7kHz
L, C, R: full range
LS, RS: 100Hz - 20kHz
LFE: none or added to L/R ( < 120Hz)
Level:
L=C=R=S(LS+RS)
Level: L=C=R=LS=RS
LFE: none
L, C, R: full range L, C, R, LS, RS: full range
Playback response
(speaker, amp)
S: 100Hz - 7kHz
LFE: none
[Table 2-1] Multi-channel formats (typical examples), Video cassette tape etc.
Surround
processing
A/D and D/A,
Compression
Record
specification
Playback
specification
Down
mixing
Multichannel media