User Manual
5
slew rate is however, preferable only to a point. A higher slew
rate will give the amplifier a wider bandwidth, and when in
excess it will ultimately result in amplification of signals even
in the radio frequency range. This will waste energy, create
distortion and also put undesirable stress on the speaker unit.
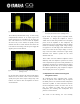
[ Fig.8 ] Circuit of a competitor amplifier. To allow Class D power supply more
time to respond to quick changes in voltage requirements, all audio goes
through a delay. Effect on sonic quality cannot be avoided with this
manipulation of the audio signal.
[ Fig.9 ] EEEngine’s “High speed buffer” is activated only when Class D power
supply is not able to keep up with sharp increases in sound. This circuitry
allows EEEngine to maintain a preferable slew rate without manipulating and
degrading the audio signal.
2. Yamaha technology
2.1. Dual mono-amplifier structure
Yamaha power amplifier technology – mechanical
design
The TXn, Tn and PC9501N series amplifiers are 2
channel amplifiers incorporating a symmetrical dual
mono-amplifier design, with each mono amplifier
having its own power supply. Dual mono-amp structure
plays an important role in achieving separation between
the two channels. Having a dedicated power supply on
each mono-amplifier minimizes interference between
the channels, preventing powerful bass notes on one
channel from taking power away from the other channel,
for example. The two power supplies operate in opposite
phases, synchronizing to cancel noise and lowering
electromagnetic interference.
[ Fig.10 ] Dual mono-amp structure. Each channel has a dedicated power
supply.
The amplifiers are also carefully designed to suppress
internal vibration within the amplifier that could have a
negative impact on sound quality. The top surface of the
heatsink is reinforced to reduce vibration to the power
transistors that are located on top of it. The heatsink
itself is fastened to the chassis side panels at numerous
strategic points with special insulators that are designed
to absorb vibration and chassis resonance that interfere
with optimum reproduction.
2.2. Full resonance switching power supply
The power supply plays a crucial role in the quality of
any amplifier. Full resonance switching power supplies
found on TXn, Tn and PC1N series amplifiers processes
two types of switching; Zero Voltage Switching and
Zero Current Switching. Full resonance power supplies
provide voltage and current waveforms with natural
curves, significantly reducing harmonic components
from switching noise. Typical switch mode power