User Manual
6
supplies employ what is typically called “hard
switching,” which induces more noise into the DC
output and gives square waveforms rich in high
frequency harmonics, requiring an additional filter to
remove them. “Soft switching” as seen in full resonance
switching on the other hand, produces natural
waveforms that are desirable for music playback.
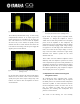
[ Fig.11 ] Current and voltage of a typical competitor power supply. Visibly
much higher noise content can be observed (circled in red). Voltage
waveform shown in yellow, and current waveform shown in blue.
[ Fig.12 ] Yamaha’s Full-resonance switching power supply. Smooth, natural
waveforms with minimum switching noise. Voltage waveform shown in yellow,
and current waveform shown in blue.
3. Behavior of the amplifier under heavy
load condition
3.1. Importance of stable 2 ohm load capability
Tn and TXn series were developed with the concept of
stable operation under 2 ohm load. We do not
necessarily suggest power amplifiers to be configured
for a 2 ohm load setup. However, we recognize that
stability under extreme low impedance is very important
for professional use power amplifiers. For example, in
the use of dual subwoofers, woofer units with nominal
impedance of about 6 to 8 ohms are typically connected
in parallel, giving the amplifier a load of 3 to 4 ohms.
Line array speakers are also often connected in parallel,
requiring stability at lower impedance. The actual
impedance curve of a speaker unit is complex and its
load varies greatly depending on frequency. A
loudspeaker’s lowest actual impedance is usually lower
than its nominal impedance. Because of this impedance
curve, an operator may unknowingly put extreme stress
to the amplifier with a source that repeatedly hits the
frequencies most demanding (lower impedance) for the
loudspeakers. Because an amplifier is put under
extremely demanding conditions at times, it is important
that there is enough headroom to keep the amplifier
from clipping.
When an amplifier clips, its output signal is distorted
and a rectangular waveform is observed. A rectangular
wave contains very high frequency and this causes voice
coils of the loudspeakers to burn out. Clipping of the
output signal, which may potentially destroy speaker
units in the system, must be prevented in a professional
audio system. An amplifier’s ability to maintain stable
operation at lower impedance is essential as an amplifier
is more likely to clip under lower impedance.