User Manual
Speaker System Design Guide for
Yamaha Sound System Simulator
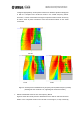
For example, to change the SPL to approximately 100 dB, you could set the amp
attenuator level to -6dB and set the input level to 10 dBu. Doing so would change
the overall SPL to 100.7 dB.
Figure 8: Adjusted level settings
¾ Given the settings shown above, the SPL at a distant point, X = 0, Y = 22.0 for
example, would be 95.4 dB. However, in an actual sound field, the level will not
decrease that much due to the effects of reflected sound. This must be taken into
account when evaluating results and configuring a system. The following section
reveals the effects of reflected sound by comparing the computed results to the
actual measured results in a hall.
; Comparison of Level Attenuations with Respect to Distance
We installed a speaker on the stage and compared level reductions for different
distances. We measured sound levels for every 2 m up to a distance of 18 m from the
speaker. We also computed sound levels for the same conditions using Y-S
3
. Figure 9
shows the results for the different distances. The horizontal (X) axis represents the
distance from the sound source, and the vertical axis represents the sound pressure
level relative to the level at 3 m from the sound source. The Y-S
3
computed results for 1
kHz attenuate steadily, but the measured results show that there is almost no
attenuation after 13 m because of sound diffusion. There is a central walkway at the
point 11 m away from the speaker, and the unique sound reflection conditions there are
evident in the plot of the measured data. The Y-S
3
computed results for 2 kHz attenuate
more gradually than those for 1 kHz. The reason for this is that the seats are on a rising
slope, so as the seats become further from the stage, they also face the speaker more
12