User's Manual
MeshNetworks
4
IAPs can be mounted on utility poles, light poles, traffic apparatus, billboards, and buildings.
Their fixed positions allow the Subscriber Device to pinpoint its location within one second.
WRs and IAPs can also be mobile, attached to emergency vehicles, utility vehicles, or fleet
vehicles. It is important to note that the WMC technology within a Subscriber Device is identical
to the WMC technology in Wireless Routers and IAPs.
The
system was designed to minimize the cost associated with deploying a mobile Internet
with end user data access rates on the order of DSL or Cable Modem. The chosen metric of
network efficiency for a data centric network is bits per second per Hertz per square kilometer
per dollar (bps/hz/km
2
/$). This metric balances the user data rates, allocated bandwidth,
coverage area, and cost. One of the most important factors in optimizing this metric is the
choice of network architecture.
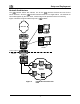
Subscriber Devices (SDs)
The MeshNetworks’ Wireless Modem Card (WMC) is
provided as a PCMCIA form factor device. The WMC is
used with an off-the-shelf IP-enabled laptop computer.
These two devices together make up a Subscriber Device
(SD).
The WMC provides access to the fixed infrastructure network
and other networks, such as the Internet, and it can also
function as a Wireless Router and repeater for other SDs.
SDs can therefore be a key part of the network infrastructure. Adding subscribers can
effectively increase the number of Wireless Routers in the network, which increases the number
of alternative paths that subscribers may utilize. This can reduce both the time and cost to
deploy network infrastructure, while also increasing the spectral efficiency and therefore the
capacity of the network. In addition, because SDs can also operate in an ad hoc peer-to-peer
mode, two or more SDs can form a network without the need for any fixed infrastructure.
Wireless Routers (WRs)
The Wireless Router (WR) is a low-cost small-sized wireless device that is primarily deployed to
seed a geographical area, extending the range between IAPs and subscribers, and to
simultaneously increase the network’s spectral efficiency. Wireless Routers provide a number
of functions in the network, such as:
• Range Extension for Subscriber Devices and IAPs
• Hopping Points for subscriber peer-to-peer
networking
• Automatic Load Balancing
• Route Selection
• Network capacity optimization through small packet
consolidation
• Fixed reference for geo-location services
The Wireless Router's small size and light weight allow it to
be mounted almost anywhere. No towers are required. WR software can be updated via over-
the-air downloads.